This is a simple example for accessing text files in MATLAB. It is always a trouble to process a signal or image in HDL directly. Using this we can convert a signal or an image into a text file and can be used to process in HDL (verilog, VHDL), etc.
First the required commands for file io are described, followed by the code example for a sine wave write and read.
If you've any problem, plz let us know. We'll assist you to overcome it. Write to us to admin@elecdude.commailto:admin@elecdude.com
First the required commands for file io are described, followed by the code example for a sine wave write and read.
fopen
Open file, or obtain information about open files
Syntax
fileID = fopen(filename)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission, machineformat)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission, machineformat, encoding)
[fileID, message] = fopen(filename, ...)
fIDs = fopen('all')
[filename, permission, machineformat, encoding] = fopen(fileID)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission, machineformat)
fileID = fopen(filename, permission, machineformat, encoding)
[fileID, message] = fopen(filename, ...)
fIDs = fopen('all')
[filename, permission, machineformat, encoding] = fopen(fileID)
fileID = fopen(filename) opens the file filename for read access, and returns an integer file identifier.
fileID = fopen(filename, permission) opens the file with the specified permission.
fileID = fopen(filename, permission, machineformat) specifies the order for reading or writing bytes or bits in the file.
[filename, permission, machineformat, encoding] = fopen(fileID) returns the file name, permission, machine format, and encoding that a previous call to fopen used when it opened the specified file. fopen does not read information from the file to determine these output values. An invalid fileID returns empty strings for all output arguments.
String in single quotation marks that specifies the name of the file to open. Can include a full or partial path.
If you open a file with read access and fopen cannot find filename in the current folder, fopen searches along the MATLAB search path. Otherwise, fopen creates a file in the current directory.
| |||||||||||||||||
String that describes the type of access for the file: read, write, append, or update. Also specifies whether to open files in binary or text mode.
To open files in binary mode, specify one of the following:
To read and write to the same file:
To open files in text mode, attach the letter 't' to the permission, such as 'rt' or 'wt+'. For better performance, do not use text mode. The following applies on Windows systems, in text mode:
|
fprintf
Write data to text file
Syntax
fprintf(fileID, format, A, ...)
fprintf(format, A, ...)
count = fprintf(...)
fprintf(format, A, ...)
count = fprintf(...)
fprintf(fileID, format, A, ...) applies the format to all elements of array A and any additional array arguments in column order, and writes the data to a text file. fprintf uses the encoding scheme specified in the call to fopen.
fprintf(format, A, ...) formats data and displays the results on the screen.
count = fprintf(...) returns the number of bytes that fprintf writes.
One of the following:
Default: 1 (the screen)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
String in single quotation marks that describes the format of the output fields. Can include combinations of the following:
Conversion characters and optional operators appear in the following order (includes spaces for clarity):
|
fclose
Close one or all open filesSyntax : fclose(fileID)
fscanf
Read data from text file
Syntax
A = fscanf(fileID, format)
A = fscanf(fileID, format, sizeA)
[A, count] = fscanf(...)
A = fscanf(fileID, format, sizeA)
[A, count] = fscanf(...)
A = fscanf(fileID, format) reads and converts data from a text file into array A in column order. To convert, fscanf uses the format and the encoding scheme associated with the file. To set the encoding scheme, use fopen. The fscanf function reapplies the format throughout the entire file, and positions the file pointer at the end-of-file marker. If fscanf cannot match the format to the data, it reads only the portion that matches into A and stops processing.
A = fscanf(fileID, format, sizeA) reads sizeA elements into A, and positions the file pointer after the last element read. sizeA can be an integer, or can have the form [m,n].
[A, count] = fscanf(...) returns the number of elements that fscanf successfully reads.
fileID
|
Integer file identifier obtained from fopen.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
format
|
String enclosed in single quotation marks that describes each type of element (field). Includes one or more of the following specifiers.
|
MATLAB CODE FOR FILE READ & WRITE:
clc;
N=6.2;
%input('Enter no of samples: ');
n=0:0.1:N;
x=10*sin(n);
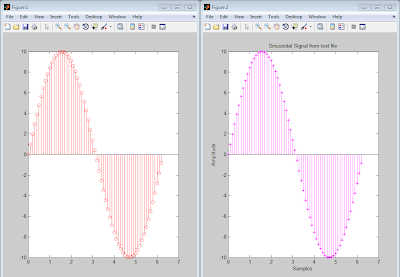
stem(n,x,'-r');
fid = fopen('sinewav.txt', 'w');
fprintf(fid, '%0.3hx\n', x);
fclose(fid);
disp('File write successful.....')
fid1 = fopen('sinewav.txt', 'r');
c = fscanf(fid1, '%g %g', [1 inf]);
disp('File is successful read...');
figure, stem(n,c,'-*m');
xlabel('Samples');
ylabel('Amplitude');
title('Sinusoidal Signal from text file');
fclose(fid1);
If you've any problem, plz let us know. We'll assist you to overcome it. Write to us to admin@elecdude.commailto:admin@elecdude.com
Viewers comments are encouraged.
This helps us to much more.
Thank you!!!







0 comments:
Post a Comment